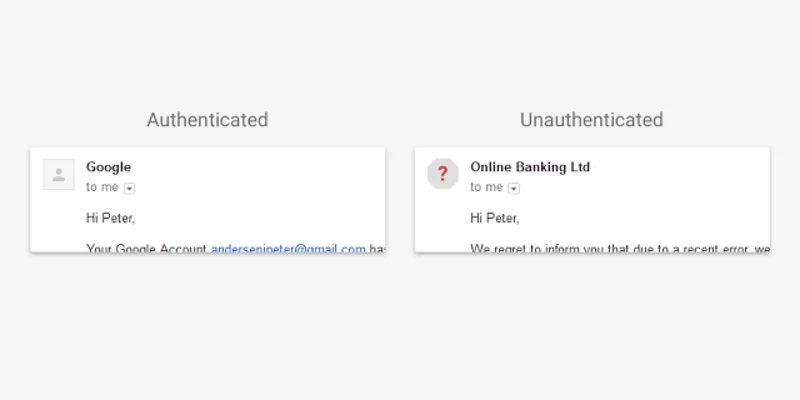
Google is rolling out a series of security features for Gmail. In a couple of weeks, Gmail users will see red question marks instead of the profile pictures of the senders, if the received message can’t be authenticated with either Sender Policy Framework (SPF) or DKIM.
The SPF is a way to identify spam messages from a sender and record it so that the future emails from the same person will be marked as spam. An enterprise customer with Google Apps can create an SPF record that identifies the mail servers that are authorized for his/her domain. DKIM is adding the digital signature to the outgoing emails. The signature will notify the server to encrypt the outgoing mail, which can be decrypted using a public key.
Similarly, the users will receive warnings while trying to open a link to a dangerous site known as phishing, malware, and unwanted software. This is an extension of the safe browsing feature already available in Google Search. However, it’s not necessary that all links that receive warnings are dangerous. Rather, the feature is included to notify the users about the potential danger and hence, to consider its safety prior to opening.

Last year, Google launched Data Loss Prevention (DLP) for Gmail for Google Apps Unlimited customers. The feature automatically checks all outgoing emails according to policies set by the Apps admin and thus, adds a layer of protection to leaking sensitive information sent through the mail.
As an addition to DLP, Google launched Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for Gmail. With this, DLP policies can analyze common image types, and extract text for policy evaluation. “Admins can enable OCR in the Admin console at the organizational-unit (OU) level for both the Content compliance and Objectionable content rules,” Google mentioned in a blog post.















