NEC Corporation has successfully developed and demonstrated a radio-over-fiber system (RoF) with a 1-bit fiber transmission method. By utilising this method, high-frequency analog signals can be transmitted using an inexpensive electrical-to-optical converter for general-purpose digital communications, thereby enabling the realisation of a compact distributed antenna unit (DA) at low cost, NEC said on Monday.
Also Read: NEC Develops RAN Autonomous Optimisation Technology
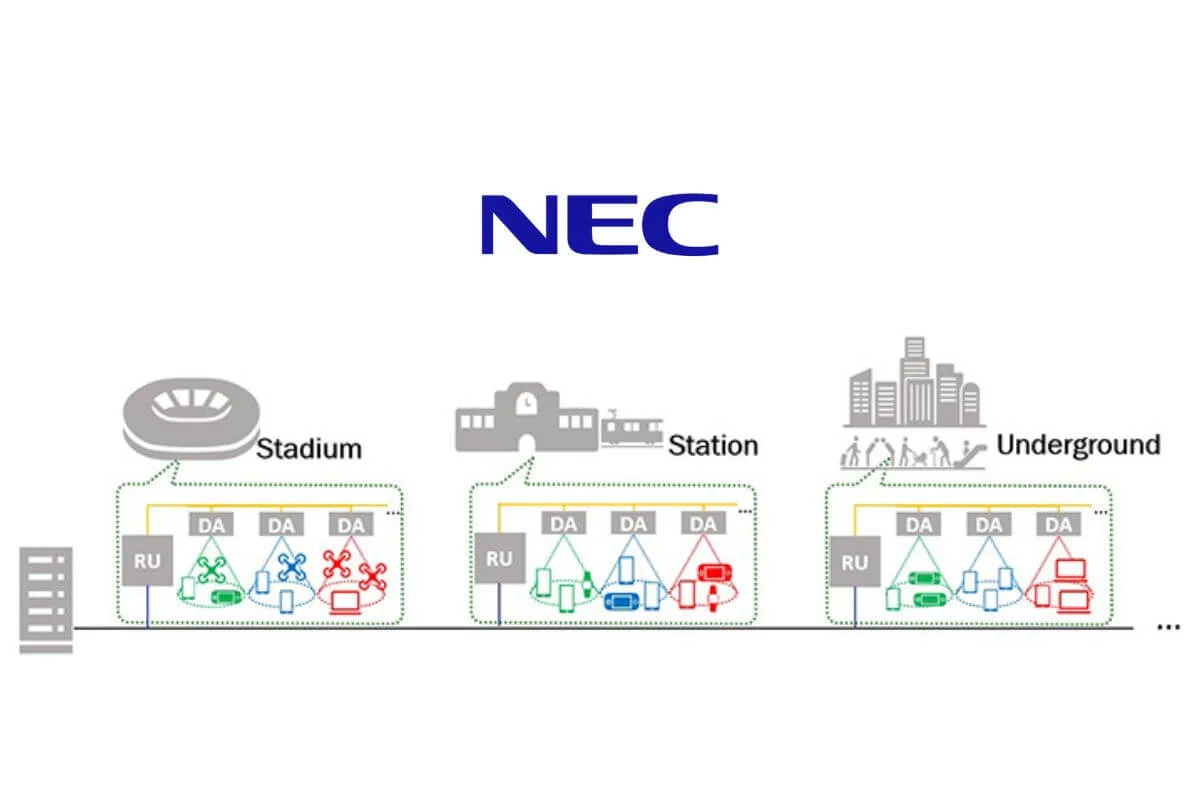
As a result, a stable millimeter-wave communication environment can be inexpensively achieved in high-rise buildings, underground malls, factories, railways, indoor facilities, and other obstacle-laden environments.
According to NEC, High-speed wireless communications leveraging millimeter-wave technology are expected to be a key technology for beyond 5G/6G. In particular, since approximately 80 percent of mobile communication traffic occurs indoors, millimeter-wave is being considered as an indoor solution.
NEC's 1-Bit RoF System
NEC explained that due to propagation loss and high linearity in the millimeter-wave frequency band, it is crucial to maintain line of sight between base stations and terminals to ensure adequate quality of service (QoS). While dense installation of distributed antenna units for direct transmission and reception of data with terminals and avoiding obstacles is known to be effective in resolving these issues, the size, power consumption, and cost of installing the required number of DA have proven to be major issues. To overcome these issues, it has developed a radio-over-fiber system (RoF) and a related transmission method, NEC said.
The newly developed 1-bit RoF system simplifies the transmission of high-frequency analog signals by converting them into 1-bit pulse signals for fiber optic transport. This approach significantly reduces both power consumption and deployment costs compared to traditional RoF systems. Unlike digital RoF systems requiring complex digital signal processing (DSP) and digital-to-analog conversion (DAC) equipment, and analog RoF systems needing costly high-linearity converters, NEC's method employs affordable, general-purpose electrical-to-optical converters, the official release said.
Also Read: NEC and NTT Successfully Test Long-Distance, High-Capacity Multicore Fiber Transmission
Technical Achievements
Key technical achievements include the development of a high Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio (SNDR) 1-bit modulator for efficient signal conversion. NEC also implemented advanced vector decomposition and digital reproduction techniques to maintain signal integrity in both downlink and uplink transmissions.
NEC said it has validated the system's performance in the 40 GHz band, confirming compliance with mobile communication standards through prototype distributed antenna units (DAUs). These compact DAUs are designed for high-density installation, enhancing line-of-sight communication capabilities in various complex environments.















