Over the years, we have come a long way in terms of using maps. Many of us just can't imagine how we would travel to a new locale without Google Maps. The live traffic feature with estimated travel duration is a fantastic feature for anyone who wants to estimate how long would it take to reach a place. All this has been possible with the democratisation of GIS (Geographic Information Systems). Just like PCs became a mainstream technology with every household having one, GIS which was once confined to large enterprises is now available for a layman to use. Beyond the simple use cases explained above, GIS has deep-rooted applications in every industry one can think of -
- Government - facilities, public works, urban planning
- Business - manufacturing, supply chain, finance, real estate
- Utilities / Communication - electricity, telecom, water
- Others - Defence, Transportation, Public Safety etc.
This article focuses on the applications of GIS in the telecom industry. For a telecom service provider, GIS acts as a strong supporting platform for
- Spectrum auctions
- Network planning and deployment
- Work order management
- Network efficiency management
While we are yet to see (to my knowledge) the application of GIS during spectrum auctions in India, Indian telecom operators are successfully using GIS for the remaining aspects.
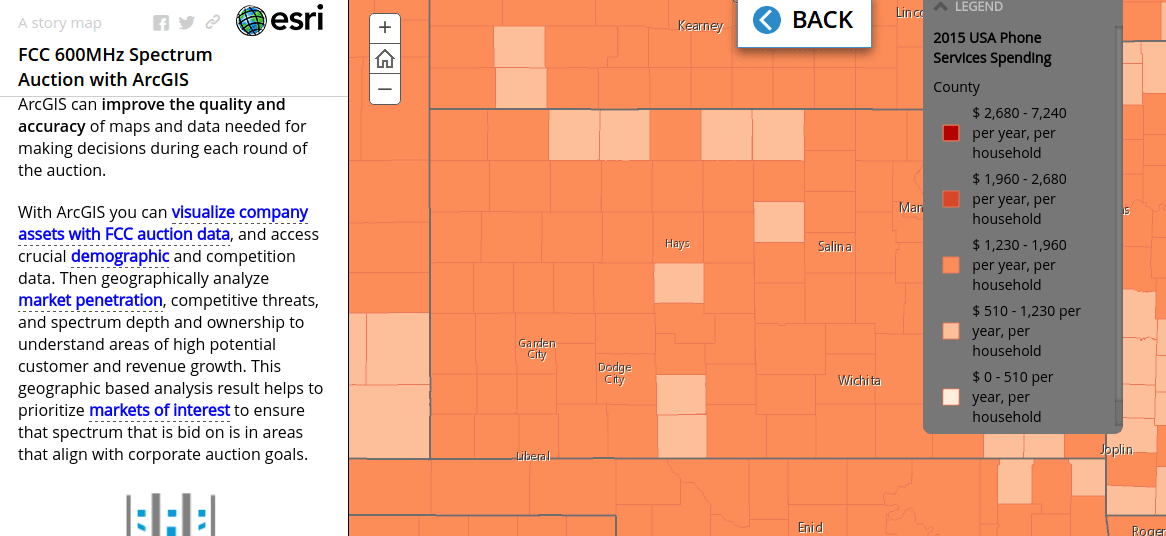
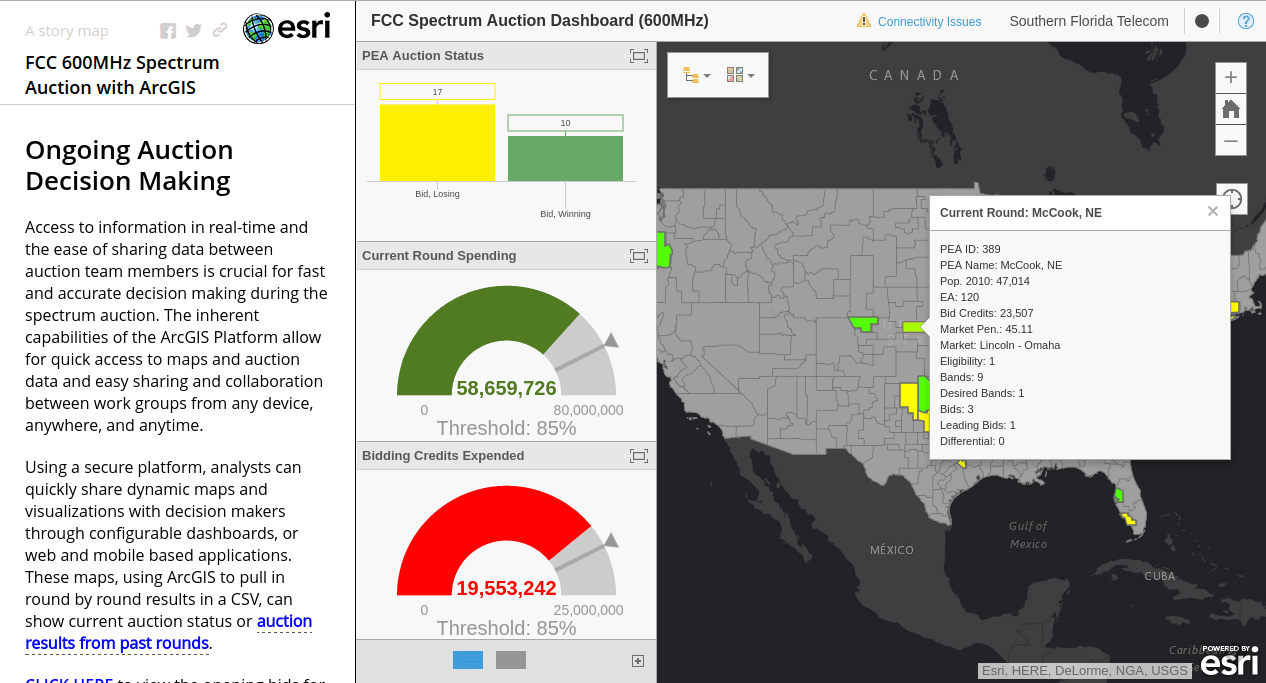
Spectrum Auctions
For the upcoming 600 MHz auctions in the United States, GIS software maker Esri has launched a solution that can help telcos come up with smarter bids after a thorough analysis. Esri claims to make pre-auction planning and decision making during the auctions a lot easier. The telco would be in a position to visualize their assets in combination with FCC data and competitor, demographic information, the key elements which drive the ultimate decisions.
Network Planning and Deployment
In the absence of standardized geospatial data availability in India, every telco is having to come up with their own strategy to make things happen. Yes, the situation is fast changing with the availability of data from Google Maps and Indian players like MapmyIndia but the availability of data which are of interest to a telco is still limited. For instance, in order to lay fiber optic cables, it is important to have data about water pipelines and cables of other service providers. Such data even if available with local bodies would be either outdated or available only in paper format. As of now telcos have to generate important information to feed into their GIS through handheld GPS devices for further processing. However, with benefits outweighing the risks telcos have taken this route and are successful.
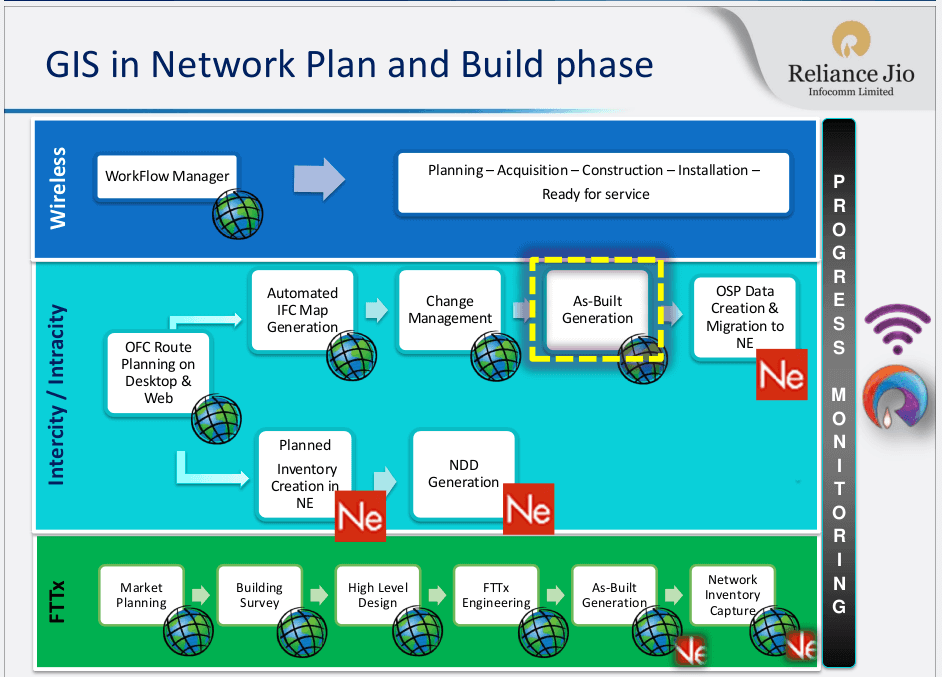
Reliance Jio
The latest example of a player using GIS extensively is Reliance Jio. In 2015, Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited was awarded by Geospatial Media and Communications for ‘Enterprise Telecom GIS’. Jio has an end-to-end business process implementation instead of GIS as a point solution utilizing extensive integration of key IT Systems like SAP FiCo, SAP MM, SAP PM, OSS, Service Assurance, etc.
Jio uses Ericsson Network Engineer and ArcGIS Suite.
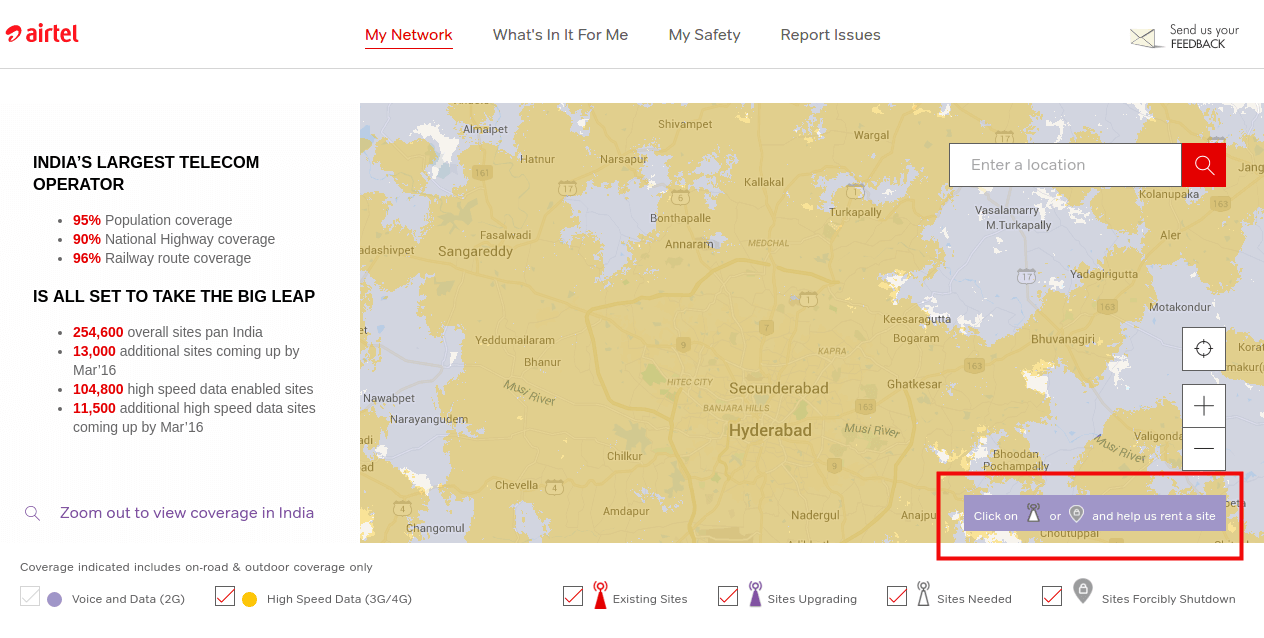
Airtel Project Leap
Airtel's Project Leap is another classic example where a telco has moved a step forward and is enabling anyone to help them find a new location for a cell site. This would not have been possible without a robust GIS.
Work Order management
With rapid growth in the number of broadband connections, issues like unintentional fiber cuts arise. To keep  customers happy it becomes really important to act fast to identify the location and fix the issue. That's when work order management comes into the picture. With every asset mapped and linked to a GIS, an operator would be able to identify the fiber cut location and immediately generate a work order to field personnel. This gets further optimized as the work order is assigned to the person nearest to the spot who can, in turn, fix the problem and report back with a picture. When done well, end users might not even know that an issue had occurred (subject to rerouting the traffic until then).
customers happy it becomes really important to act fast to identify the location and fix the issue. That's when work order management comes into the picture. With every asset mapped and linked to a GIS, an operator would be able to identify the fiber cut location and immediately generate a work order to field personnel. This gets further optimized as the work order is assigned to the person nearest to the spot who can, in turn, fix the problem and report back with a picture. When done well, end users might not even know that an issue had occurred (subject to rerouting the traffic until then).
Network Efficiency Management
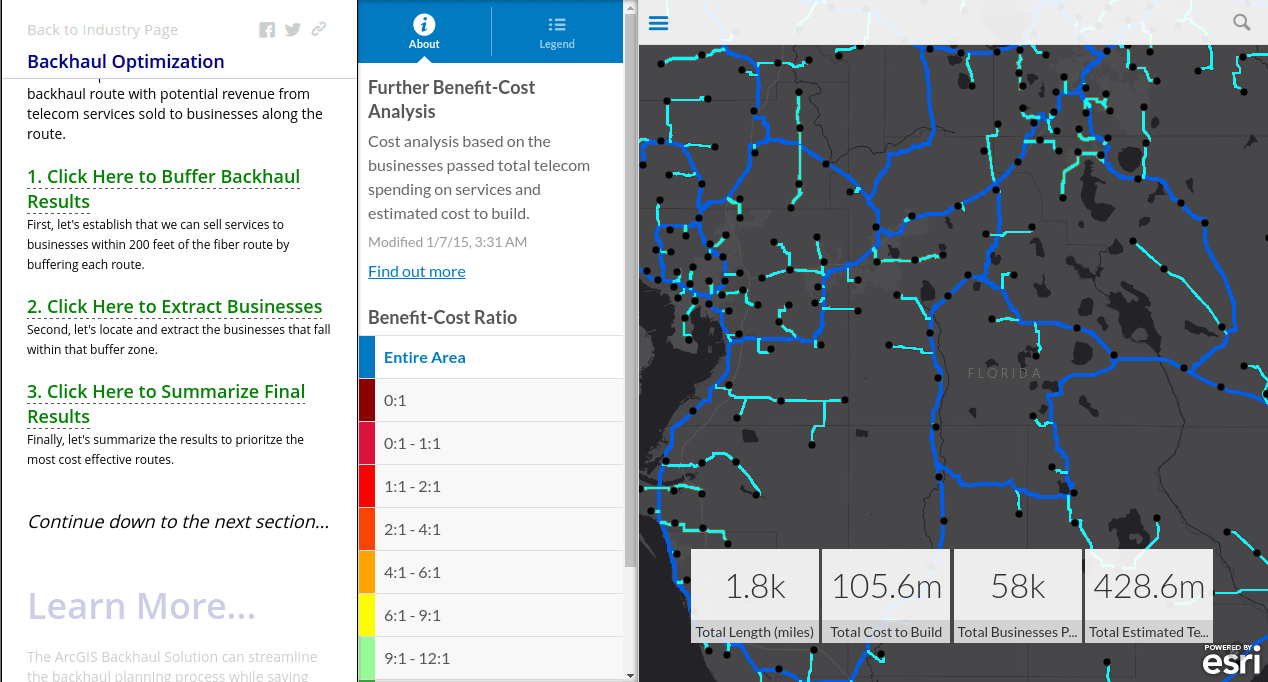
With ever growing demand for data and the new found problem of call drops plus TRAI order to penalize telcos for the same, network efficiency is of paramount importance. Just like for network planning, network efficiency can be improved by leveraging GIS. Telcos already have sufficient information with which they can easily identify overloaded cell towers and installation of small cells could be a good step to curb call drops. On the growing data consumption, strengthening the backhaul can be an effective solution.
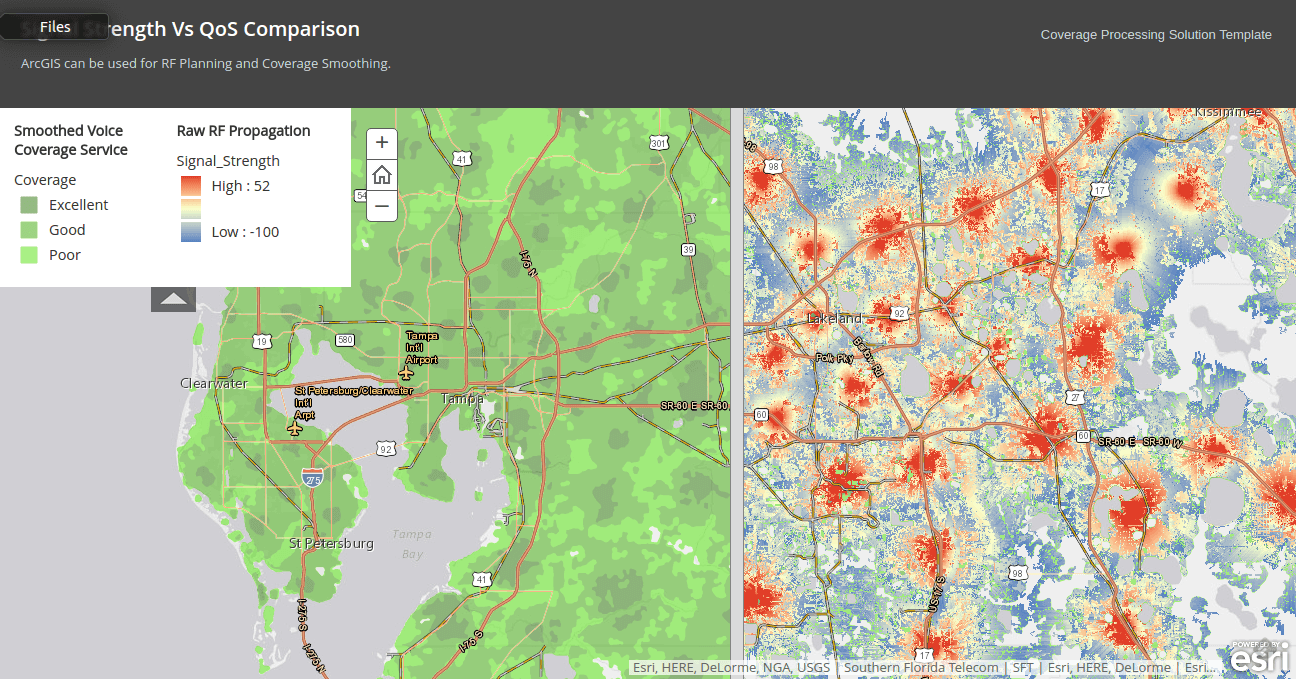
RF Planning and Coverage smoothing can also be achieved using GIS.
Conclusion
GIS can be regarded as the backbone for any telecom service provider's day to day operations. This rapidly evolving technology has enabled telcos to roll out networks faster than ever before and ensure that every customer gets a satisfactory experience.